
12 Jan, 2026
High-Tech Jungle: The Role of Technology-Based Monitoring in Tiger Conservation and Tourism
The jeep engine cuts off. Silence settles over the Sal forest, broken only by the rustle of dry leaves and a distant langur call. Somewhere nearby, a tiger moves out of sight. This moment of anticipation draws travellers into India’s wild landscapes. Not long ago, such sightings relied on instinct, chance, and faint pugmarks pressed into the earth. Today, while the thrill of safari remains the same, tiger tourism in India has entered a new era, shaped quietly by data, sensors, and satellite signals.
Deep in the forest, camera traps, GPS systems, thermal surveillance, and artificial intelligence work nonstop. Technology-driven monitoring in tiger conservation now forms the backbone of wildlife protection in India. It helps authorities track tiger populations, prevent poaching, and manage fragile habitats effectively. This digital change does more than protect India’s national animal. It also redefines how safaris operate, making wildlife encounters safer, more ethical, and more sustainable. Technology now plays a central role in tiger conservation and tourism in India, from regulating tourist zones to reducing human-tiger conflict.
India’s tiger conservation strategy is anchored in one of the world’s most ambitious wildlife protection programs. Under Project Tiger, launched in 1973 and currently implemented across more than 50 tiger reserves, technology-based monitoring has become a critical pillar of protection. Tools such as camera traps, GPS-enabled patrol systems, and real-time surveillance are now officially integrated into management frameworks guided by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA). This institutional backing ensures that technology in tiger conservation is not experimental but policy-driven, regulated, and continuously audited.
This blog explores how technology-based monitoring enhances conservation efforts and improves the safari experience. It also examines how innovation shapes the future of tiger tourism, balancing wildlife protection, visitor experience, and community livelihoods in some of India’s most iconic tiger landscapes.
From Traditional Tracking to Technology-Enabled Monitoring
For decades, tracking tigers relied on indirect signs like pugmarks, scratch marks, and sightings. While useful, these methods often lacked accuracy and consistency. The move towards technology-enabled monitoring was a turning point in wildlife conservation. It allowed for precise population counts, territory mapping, and real-time threat detection.
Modern monitoring systems help forest managers see not only how many tigers are out there but also where they move, breed, and interact. This data-driven approach is key to strengthening tiger conservation across India’s protected areas.
The "Big Three" Technologies Protecting India’s Tigers
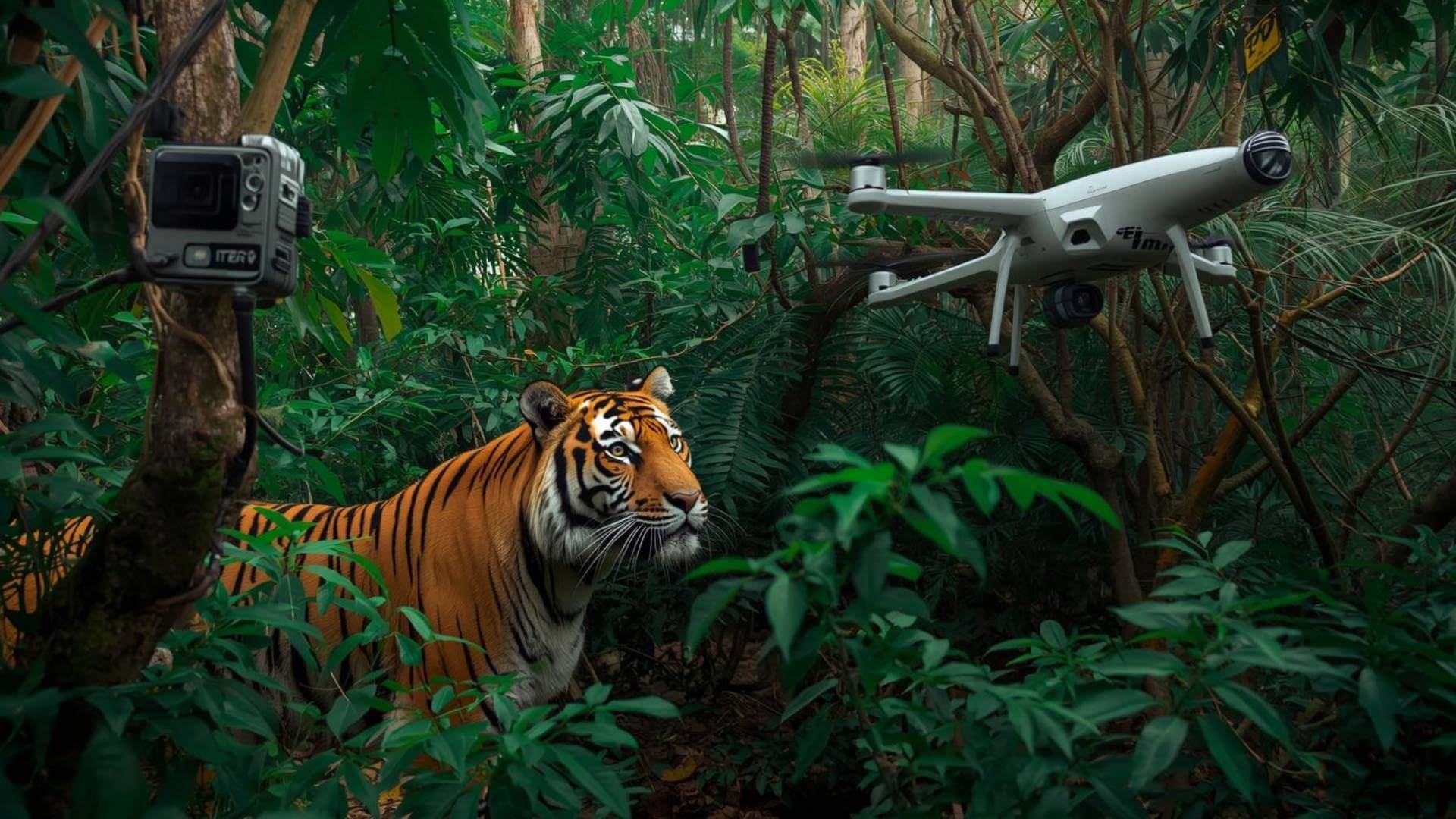

When you visit a national park, you are entering a highly surveilled zone. Here are the tools working silently behind the scenes.
- Camera Traps (The Silent Observers): These motion-sensitive cameras attached to trees act as the forest's 24/7 eyes, taking a photo whenever an animal crosses their infrared beam. Every tiger has a unique stripe pattern, similar to a human fingerprint. Software analyzes these images to identify specific individuals, like distinguishing T-120 from T-86. This precise identification is an essential part of technology-driven monitoring. It ensures that the lineage stories and territorial facts your guide shares are based on verified data rather than guesswork. Today, camera trap-based identification forms the backbone of India’s All India Tiger Estimation exercises, enabling scientists to estimate population trends with far greater accuracy than earlier pugmark-based methods.
- M-STrIPES (Smart Patrols): The "Monitoring System for Tigers-Intensive Protection and Ecological Status" is a GPS-enabled mobile app used by forest guards to log patrol routes and sightings in real time. It acts like a digital Fitbit for the forest department, allowing park directors to see precisely which trails have been covered and which vulnerable areas were missed. This digital accountability is crucial for strengthening tiger conservation. It ensures that the security net against poachers is tight and the jungle you visit is closely monitored. M-STrIPES is now deployed across most tiger reserves in India, creating one of the largest digital patrolling datasets in wildlife conservation globally.
- E-Eye Surveillance (The Electronic Fence): Used mainly in sensitive areas such as Jim Corbett National Park, the E-Eye system comprises thermal and infrared cameras mounted on tall towers to create an invisible electronic fence. These cameras detect the heat signatures of any moving object heavier than 20 kg, whether it is a poacher or a tiger. They instantly send live video alerts to a central control room. This fast response system shows the positive impact of technology on tiger conservation. It helps prevent illegal entry and keeps tigers from wandering into human settlements. In landscapes where tiger habitats overlap with villages, thermal surveillance systems like E-Eye have significantly reduced response times to potential conflict situations, helping authorities intervene before incidents escalate.
Technology and the Evolution of Tiger Tourism in India

Tiger tourism in India operates under strict regulatory frameworks, where conservation priorities override commercial interests. Technology-driven monitoring has strengthened this balance by allowing tourism to function within scientifically defined ecological limits.
Modern tiger tourism in India has evolved beyond lucky sightings and crowded safari routes. With technology-driven monitoring, wildlife tourism now relies on data, ethics, and long-term conservation goals, rather than just chance.
Advanced tracking systems help forest departments create safari zones based on tiger movement patterns, breeding cycles, and habitat sensitivity. This approach allows tourists to enjoy the forest responsibly without disturbing wildlife. Technology also supports real-time decision-making, enabling authorities to limit access to sensitive areas when needed, protecting tigers while maintaining high-quality tourism.
For visitors, this results in fewer vehicles per zone, better-trained guides, and a greater chance of meaningful sightings. More importantly, it builds trust. Tourists understand that their visit directly supports tiger conservation and tourism in India, rather than leading to exploitation.
As a result, technology is not only protecting tigers but also shaping the future of tiger tourism in India, making it more sustainable, educational, and conservation-focused.
How Technology Enhances Your Safari Experience
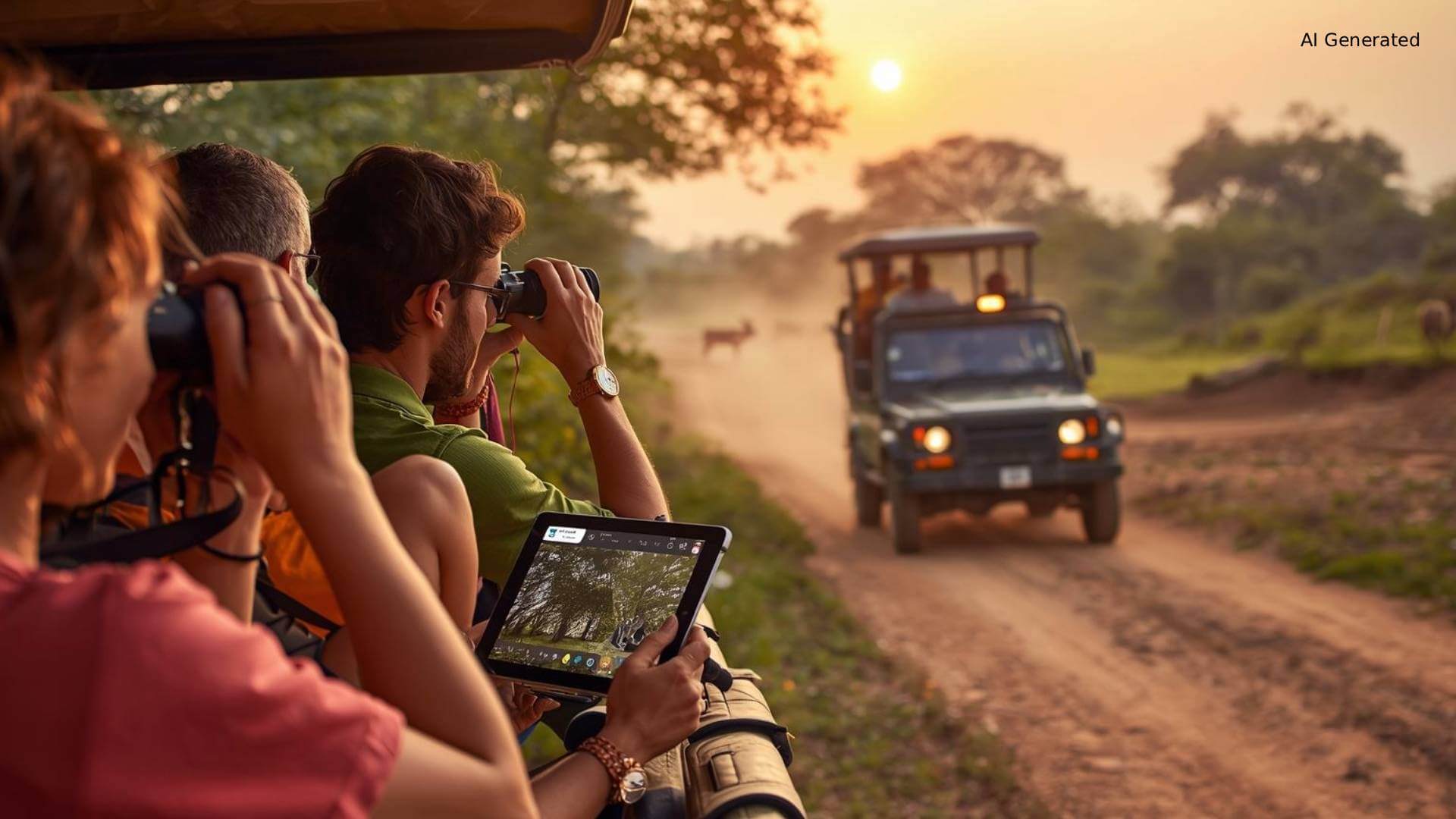

You might ask, “I’m here for a holiday. Why does backend data matter to me?” The answer is simple. Better technology leads to better, more responsible safaris.
The impact of technology on tiger conservation directly shapes how tourism operates, improving both wildlife protection and visitor experience.
- Predictive Sightings: By analyzing movement patterns and habitat use, park managers can regulate zones based on real-time animal activity. This thoughtful planning increases the likelihood of sightings while reducing unnecessary vehicle pressure. These decisions are typically taken by park directors and wildlife biologists using long-term movement data, ensuring that tourism routes adapt to animal behavior, not the other way around.
- Ethical Encounters: GPS collars help officials monitor stress levels, especially for tigresses with cubs. If stress levels rise, routes change quickly, ensuring you see wildlife respectfully, without causing disruption. This approach aligns with global wildlife tourism guidelines that prioritize minimal disturbance, especially during sensitive breeding and cub-rearing periods.
The Upgrade: "In 2023, E-Eye thermal cameras in Corbett detected a tiger wandering near the park boundary at 2:00 AM. Authorities were alerted instantly and were able to redirect the animal before it reached a neighboring village.".
- Safety & Sustainability: Early warning systems prevent tigers from moving toward resort areas or villages. Ths reduces conflict and supports a safer ecosystem, securing the future of tiger tourism in India for travelers and local communities.
The result is a safari experience that feels natural, calm, and meaningful. Conservation works quietly in the background so the wilderness remains wild.
Socio-Economic Impacts of Tiger Tourism on Local Communities in India

Conservation cannot exist in isolation. Tiger tourism has a significant impact on local communities in India, and technology is improving the situation.
The move to technology-based monitoring has led to new job opportunities. Local young people, who previously relied on subsistence farming or were at risk of joining poaching networks, are now being trained as "Tech Assistants." They fly drones, handle camera trap data, and monitor sensor feeds.
When a local villager has a stake in wildlife protection, the tiger shifts from being a threat to becoming an economic asset. This shift highlights the positive socio-economic impacts of tiger tourism on local communities in India, ensuring that conservation benefits both the forest and the communities living around it.
By linking livelihoods directly to conservation outcomes, technology-based monitoring helps shift local economies away from extractive practices toward long-term, skill-based employment within the conservation ecosystem.
Where to Witness Conservation Tech in Action

These reserves are frequently cited in conservation studies and management discussions for their early adoption of technology-assisted protection measures. Want to see how technology supports tiger conservation and tourism in India firsthand? Plan your next trip to these pioneering reserves:
- Ranthambore National Park (Rajasthan): Famous for its radio-collared tigers. Guides here are exceptional at interpreting tracking data to predict movement.
- Jim Corbett National Park (Uttarakhand): The home of the E-Eye surveillance system.
- Kaziranga National Park (Assam): A leader in using drones to monitor rhinos and tigers across floodplains.
The Verdict: A Future of Co-Existence

As conservation challenges grow more complex, technology will continue to play a defining role in protecting India’s tigers. Yet its true value lies in how responsibly it is used. When data supports decisions, when tourism respects ecological limits, and when communities benefit from protection rather than exploitation, conservation becomes durable. In this model, technology does not replace human effort; it strengthens it.
Ready to hear the roar? Plan your responsible Tiger Safari with us today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does radio-collaring hurt the tiger?
No. Modern radio collars are lightweight, making up less than 2% of the tiger's body weight. They are designed to drop off automatically after a set period. They are essential for studying behavior and making sure technology positively impacts tiger conservation.
How does technology reduce human-wildlife conflict?
Tech helps create "virtual fences." Thermal cameras and SMS alert systems warn forest officials when a tiger moves toward a village, allowing them to drive the animal back before a conflict occurs.
What is the M-STrIPES app?
M-STrIPES is a GPS-based app used by Indian forest guards to record patrol routes and biological data. It ensures that wildlife conservation efforts are based on data and that no part of the forest remains unprotected.
Can tourists see the data from tiger monitoring?
While raw data is kept confidential to prevent poaching, the results are shared through interpretation centers in parks and by knowledgeable guides. They use this information to explain tiger behavior during your safari.
Other Interesting Blogs to Read
- Rani Machli: Honoring the Legacy of Ranthambore’s Queen Tigress
- Best Jungle Safaris in India
- Why We Celebrate International Tiger Day?
- Best Places to Visit in Rajasthan
- Best Wildlife Resorts to Stay in Ranthambore
- Information Trinetra Ganesh Temple Ranthambore
- Ranthambore National Parks Latest News Updates
- Best Luxury Resorts in Ranthambore National Park
- Peacock Flying in Ranthambore National Park
- Take a Jungle Safari at These 10 Best Wildlife Destinations in Summer Season & Get the Best of Wildlife Adventure
- The Inspiring Story of How Aditya & Poonam Singh Made a Lush Forest Out of a Barren Land in Ranthambore
- Why Should We be Teaching Wildlife Conservation in Schools?
- Do’s and Don’ts of Staying Safe Around Wildlife
- Human – Wildlife Conflict in Concrete Jungle
- 20 Facts You Probably Didn’t Knew About Tigers
- Wildlife Conservation Initiatives by Indian Government
- Experience Golden Triangle India with Ranthambore Tiger Safari
- 10 Reasons to Visit Ranthambore Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan
- In Pictures: Showcasing India’s Endangered Species
- My Experience at Ranthambore National Park- Sundeep Kheria
- Top 5 Star Hotels in Ranthambore Tiger Reserve
- Photography Tour in Ranthambore National Park
- Rajiv Gandhi Regional Museum of Natural History








 Share
Share Home
Home Packages
Packages Book Now
Book Now